Akshay K. Burusa

I am a robotics and computer vision engineer with experience in both research and real-world deployment. I am finishing my PhD at Wageningen University, Netherlands, in the field of robotics and computer vision, addressing occlusion challenges for visual perception. I like to work at the intersection of technical innovation and real-world impact.
Professional interests: Robotics, Computer vision, 3D scene understanding and mapping, Autonomous navigation, SLAM, and Sensor fusion
View my LinkedIn profile
Robotics and Computer Vision Engineer
Education
- Ph.D. Candidate, Robotics and Computer Vision (2025)
Title: Active Vision for Agricultural Robotics
Wageningen University and Research, The Netherlands - M.Sc., Systems Control and Robotics (Sep 2017)
KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden - B.Sc., Electrical and Electronics Engineering (May 2017)
Anna University, India
Skills
- Software: Robotic Operating System (ROS1/ROS2), PyTorch, MoveIt, OpenCV, Open3D, COLMAP, Git, Docker, Gazebo
- Coding: Python, C++, MATLAB
- Hardware: Nvidia Jetson Orin, ABB 6DoF manipulator, OAK-D RGB-D camera, Realsense RGB-D and LiDAR cameras, Robotiq 2-finger gripper, Arduino
- Languages: English (full professional proficiency), Planning to learn Dutch, Telugu (native), Tamil, Hindi, German (basic, had B1 proficiency in the past)
Work Experience
AI and Computer Vision Engineer (Apr 2025 - Present)
Track32, The Netherlands
- Developed skills for deploying AI and Computer Vision algorithms on edge devices like Jetson Orin and OAK-D
- Designed, developed the software architecture, and handled client communication for multiple real-world projects involving ROS2 and computer vision solutions
- Aimed at optimising AI models through quantization (e.g. TensorRT)
- Worked with ROS2, Python, trained and deployed vision models, ONNX and TensorRT conversion, Docker for easy deployment, ClearML for MLOps
PhD Candidate (Oct 2019 - Aug 2024)
Wageningen University and Research, The Netherlands
- Worked on visual perception for a tomato harvesting robot that operated autonomously in a greenhouse (NWO project FlexCRAFT)
- Addressed the challenge of occlusion, which is a major reason of failure for harvesting and de-leafing robots
- Trained deep neural networks for semantic segmentation and keypoints detection to identify plant parts
- Developed active vision strategies that enabled robots to plan camera viewpoints that were occlusion-free and improved the efficiency and accuracy of perception
- Tested the active vision strategies in a tomato greenhouse and showed that it outperformed traditional methods
- Wrote the base code using ROS, C++, and Python for a collaborative team of 10 PhDs and 3 Postdocs and maintained it on Git
Robotics Software Developer (Oct 2017 - Sep 2019)
Geo-konzept GmbH, Germany
- Applied autonomous vehicle and computer vision technology to agricultural and forestry applications
- Developed software to reconstruct 2D crop-quality maps of farms by geometrically correcting and aligning multi-spectral drone images
- Developed a visual-inertial odometry algorithm to track the position of a wood harvesting vehicle under dense forest cover when GPS was unreliable
Projects
Active vision for robotic harvesting and de-leafing of tomato plants
Robotic harvesting and de-leafing is extremely challenging due to occlusion of plant parts by leaves. I designed multiple novel algorithms in my PhD to address the challenge of occlusion and improve the perception of plant parts by robots. The algorithms use active vision, a strategy to intelligently plan the camera viewpoints such that occlusion can be avoided and perception can be improved.
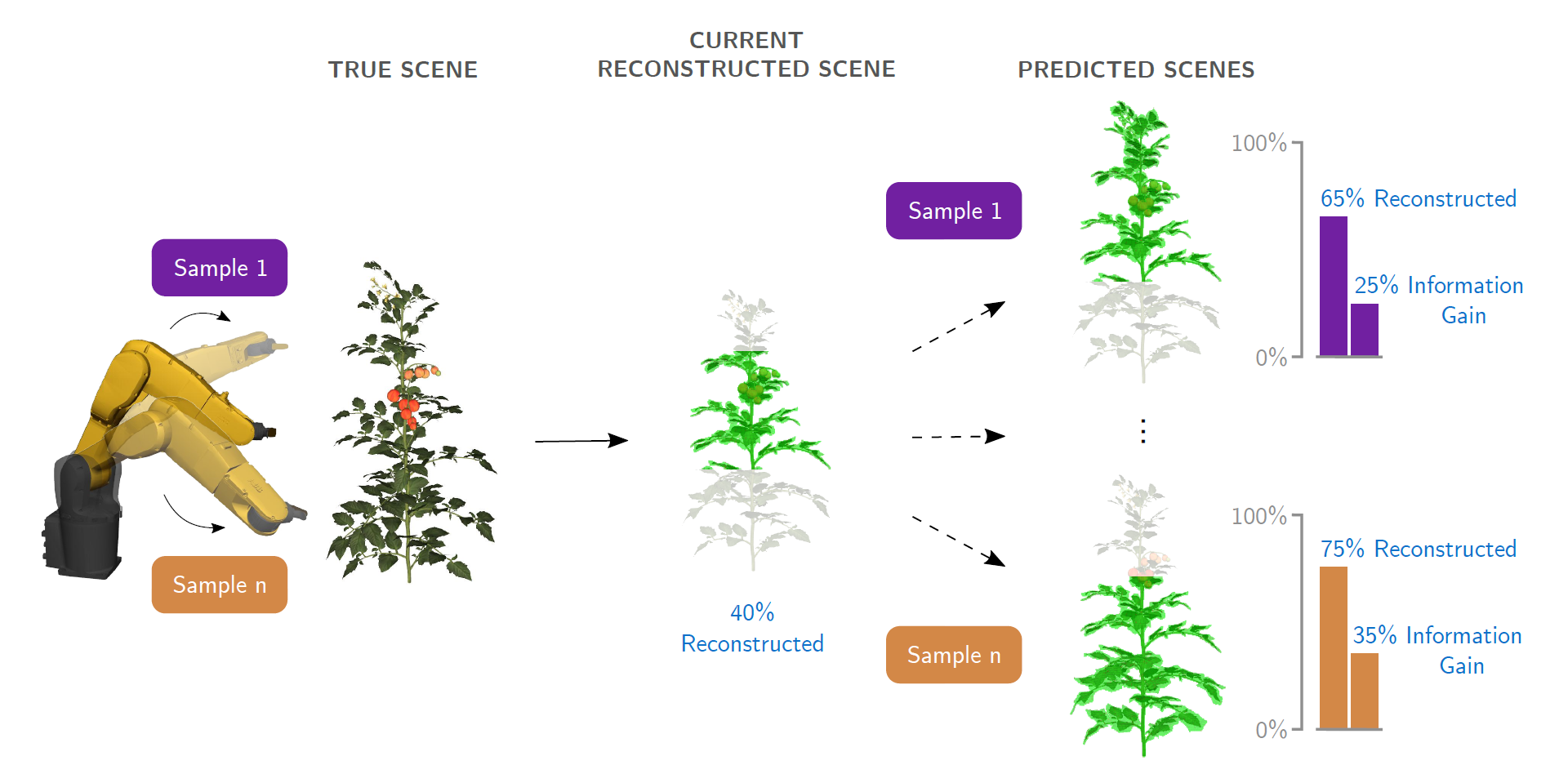
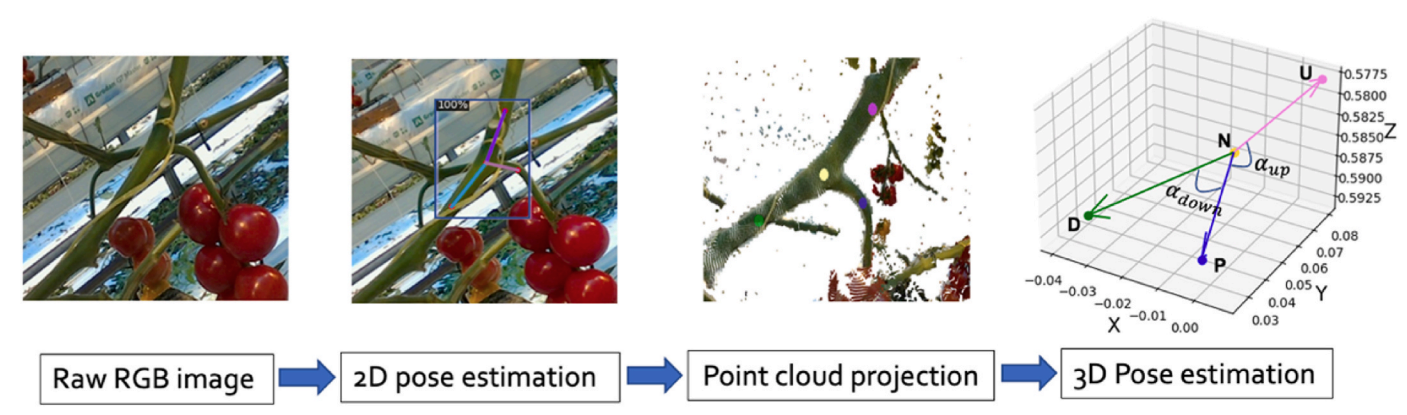
Detection and pose estimation of fruit and leaf node for automated harvesting and de-leafing
For automated harvesting and de-leafing of plants, robots need to detect the fruit and leaf nodes and estimate their pose. The pose is used by the robot to appraoch the node and make a cut. In this project, I worked on a deep learning algorithm to identify the semantic mask and keypoints of the fruit and leaf nodes. The keypoints were then projected to 3D to estimate the pose of the nodes. This approach was tested and shown to work really well in a tomato greenhouse. It can potentially lead to high success rates in robotic harvesting and de-leafing.
Pose estimation of chicken pieces for robotic pick-and-place
Automated picking and placing of chicken pieces using a robot is extremely challenging due to their deformable and slippery nature. For successful pick-and-place operation, the robot must grasp the chicken pieces at rigid and stable parts of the chicken piece. For this, it is important to detect the chicken pieces and estimate their pose and keypoints, which can then be used for grasping. In this project, I helped with a deep learning network to detect the keypoints and estimate the pose of chicken pieces. The pick and place operation was tested in an ABB 6DoF robotic arm with a 2-finger gripper.

Publications
Peer-reviewed journal publications
- Burusa, A. K., Scholten, J., Wang, X., Rapado-Rincon, D., van Henten, E. J., & Kootstra, G. (2024). Semantics-aware next-best-view planning for efficient search and detection of task-relevant plant parts. Biosystems Engineering, 248 , 1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2024.09.018
- Burusa, A. K., van Henten, E. J., & Kootstra, G. (2024). Attention-driven next-best-view planning for efficient reconstruction of plants and targeted plant parts. Biosystems Engineering, 246 , 248–262. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2024.08.002
- Rapado-Rincon, D., Burusa, A. K., van Henten, E. J., & Kootstra, G. (2024). A comparison between single-stage and two-stage 3d tracking algorithms for greenhouse robotics. Sensors, 24(22), 7332. doi: 10.3390/s24227332
- Raja, R., Burusa, A. K., Kootstra, G., & Van Henten, E. J. (2024). Advanced robotic system for efficient pick-and-place of deformable poultry in cluttered bin: A comprehensive evaluation approach. IEEE Transactions on AgriFood Electronics, 2 , 355–371. doi: 10.1109/TAFE.2024.3379190
- Ci, J., Wang, X., Rapado-Rincon, D., Burusa, A. K., & Kootstra, G. (2024). 3d pose estimation of tomato peduncle nodes using deep keypoint detection and point cloud. Biosystems Engineering, 243 , 57–69. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2024.04.017
- Senden, J., Hollands, K., Rapado-Rincon, D., Burusa, A. K., Herremans, B., Bruyninckx, H., & Van De Molengraft, R. (2023). Multi-hypothesis tracking in a graph-based world model for knowledge-driven active perception. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 8 , 5934–5941. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2023.3300282
Peer-reviewed conference publications
- Burusa, A. K., van Henten, E. J., & Kootstra, G. (2024). Gradient-based local next-best-view planning for improved perception of targeted plant nodes. In 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) (pp. 15854– 15860). IEEE. doi: 10.1109/ICRA57147.2024.10610397
Peer-reviewed journal submissions
- Wang, X., Burusa, A. K., Rapado-Rincon, D., Versmissen, T. A. W., van Henten, E. J., & Kootstra, G. (2024). Multiple object tracking with multi-view active vision to effectively find plant nodes in a cluttered tomato greenhouse. Submitted for publication in Computers and Electronics in Agriculture
- Ci, J., Wang, X., Burusa, A. K., Henten, E. J. v., & Kootstra, G. (2024). Ssl-nbv: A self-supervised-learning-based next-best-view algorithm for efficient 3d plant reconstruction by a robot. Submitted for publication in Computers and Electronics in Agriculture
- Raja, R., Pacheco, L. A. P., Burusa, A. K., van Henten, E. J., & Kootstra, G. (2024). Real-time 6-dof grasping of deformable poultry legs in cluttered bins using deep learning and geometric feature extraction. Submitted for publication in Computers and Electronics in Agriculture